Asexual Reproduction
7.14.B compare the results of uniform or diverse offspring from sexual reproduction or asexual reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
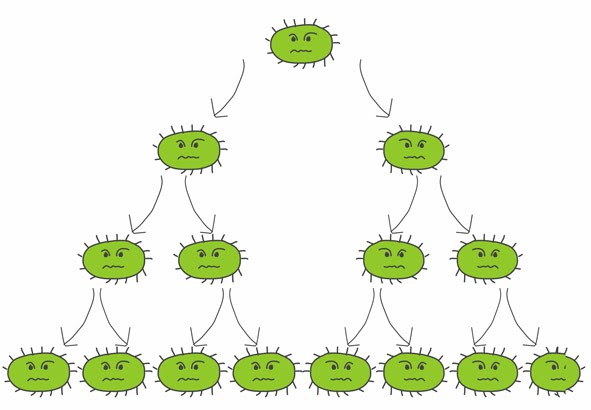
1 parent, occurs in all prokaryotes and some eukaryotes
- Occurs in PROKARYOTES
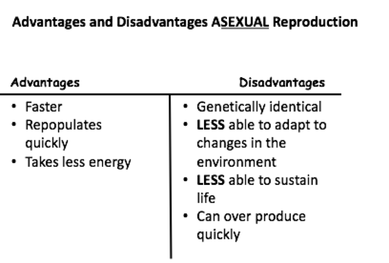
- Genetically identical
- 1 parent
- Uniform offspring – genetically identical
- No genetic variation
- All have the same traits
- Not able to adapt to changes in the environment.
- Happens quickly and can overpopulate
- Eubacteria
- Archaebacteria
- Some plants - A few examples are; ivy, potatoes, carrots
- Some animals - coral, jellyfish and hydra are reproduce by budding.
|
|
|
|
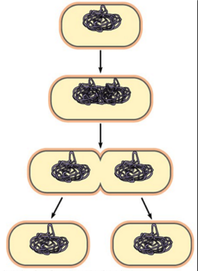
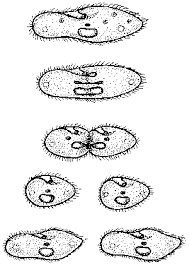
Asexual Reproduction - Binary Fission
split into two genetically identical pieces.
- parent
- splits into two genetically identical organisms
- the parent organisms splits into two pieces, making an identical copy of itself
Example: Bacteria
- splits into two genetically identical organisms
- the parent organisms splits into two pieces, making an identical copy of itself
Example: Bacteria
Asexual Reproduction - Budding
- 1 parent
- splits into two genetically identical organisms.
- small buds appear on the body of the parent and develop into two organisms.
Examples: Animals (coral, jellyfish and hydra)
Fungi - yeast
- splits into two genetically identical organisms.
- small buds appear on the body of the parent and develop into two organisms.
Examples: Animals (coral, jellyfish and hydra)
Fungi - yeast
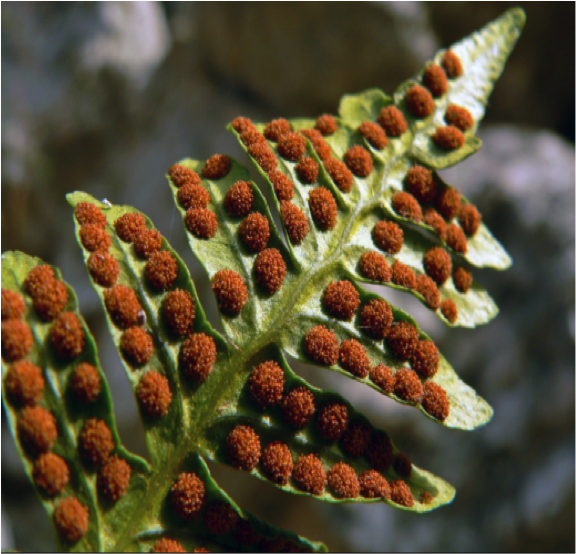
Aexual Reproduction - Spores
- 1 parent
- genetically identical to parent
- develops spores on the leaves (in a leaf it looks like little dots.)
Example: when the leaf falls off the spores/seeds are spread to the soil.
Asexual Reproduction - Fragmentation
- 1 parent
- genetically identical to parent
- a new organism grows from a fragment/a piece of the parent
Example: starfish and some worms
- genetically identical to parent
- a new organism grows from a fragment/a piece of the parent
Example: starfish and some worms
Asexual Reproduction - Vegetative Propagation
- 1 parent
- genetically identical to parent
- only in plants
- a new pant forms form a piece of the parent
Example: if you a take the eye of a potato and place it in the soil, a potato will form.