Watershed
A watershed is a place where water drains into one spot, such as a lake or ocean.
* Everyone lives in a watershed. The animals, birds, and fish do too.
* You influence what happens in your watershed, good or bad, by how you treat
the natural resources, the soil, water, air, plants, and animals.
* Everyone lives in a watershed. The animals, birds, and fish do too.
* You influence what happens in your watershed, good or bad, by how you treat
the natural resources, the soil, water, air, plants, and animals.
|
|
|
|
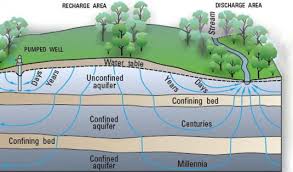
Aquifers
|
|
|
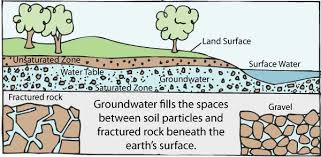
Groundwater
|
|
|
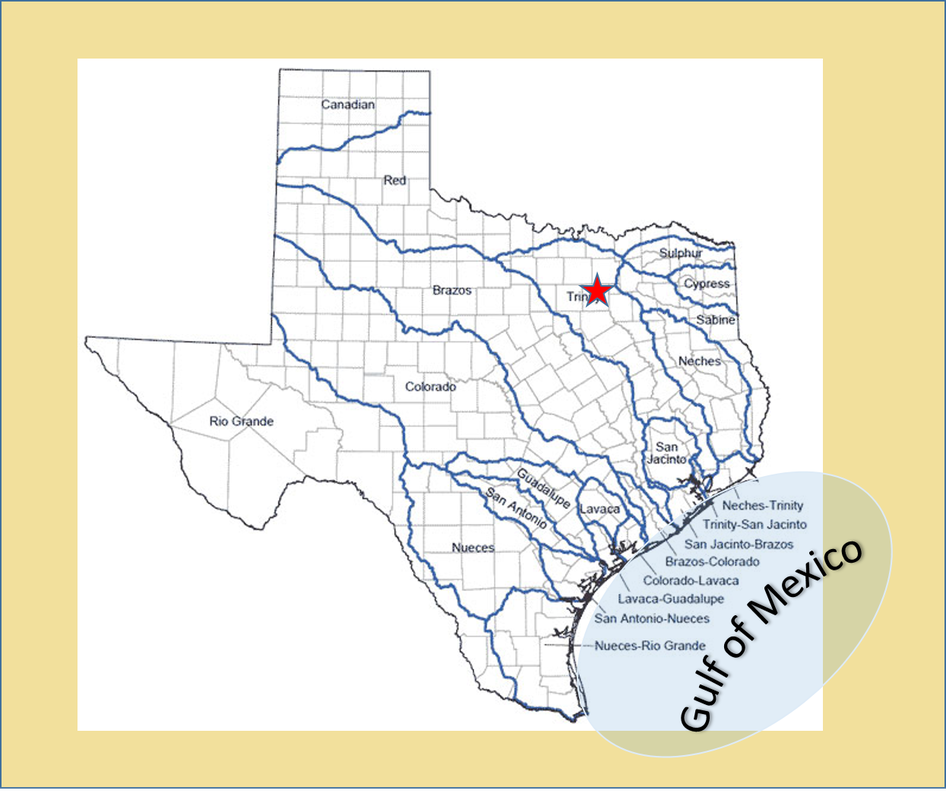
Texas Watersheds
Non-point & Point of Source Water Pollution
Non-Point of Source |
Point of Source Pollution |
|
The specific source of the pollution can't be identified. This is the greatest cause of pollution.
|
We can point to the source of the pollution. We know where the pollution came from.
|
|
Water Quality - How do we know the quality of water?
|
|
Disclaimer: The purpose of watching this video isn't to promote the product Qure. The purpose is to learn the meaning of PH and the PH scale and that the PH of water should be 7.
|