Weathering - Breaks it down.
|
Physical Weathering
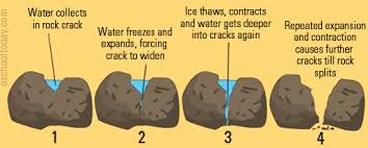
- Moving water breaks up rock on beaches to form sand. - Water seeps into crevices in rock. When it freezes, the ice cracks the rock. - Wind carries small particles such as sand. The sand smooths away surface rock, just like sandpaper smooths wood. Physical Weathering changes, aka mechanical |
|
|
Chemical Weathering
Chemicals in the environment break it down. |
|
|
Oxygenation (rust) occurs when the oxygen combines with moisture causing a reaction called iron oxide breaking it down.
|
CO2 combines with the water in the rock forming carbonic acid. This acid reacts to minerals in the rock to break it down. This is how most caves are formed.
|
Acid/rain pollution breaks down rock. This is why old tombstones and statues look like they are dissolving.
|
Biological Weathering
Living things such as animals, insects, plants & people break down the rock.
|
|
|
|